Chinese massage involves applying various manipulations to stimulate the soft tissues, stretch the muscles and mobilize the joints. When massage is used on specific body regions, the pressure acting locally can promote blood circulation and remove stagnations, facilitate soft tissues repairing and correct bone and joint deformities. In addition, despite being applied to the surface of the body, massage creates signals that affect the transmission of body fluids, qi (vital energy) and blood, which in turn regulate the functions of the internal organs.
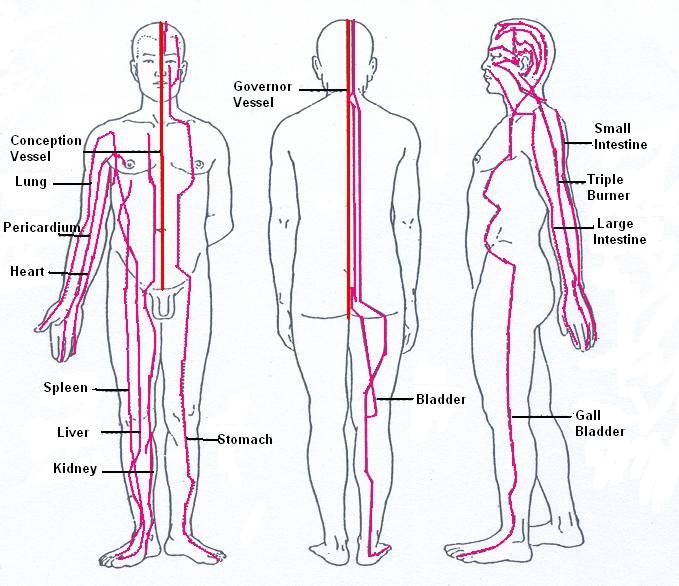
Distributions of the fourteen meridians
Chinese massage provides a kind of physical stimulation to the body, its therapeutic benefits are achieved through different manipulations to create tissue reactions, adjust the nerve reflex or body fluid activities. For example, when applying friction method to stimulate the skin, it can facilitate the falling of aging epithelial cells, promote the secretions of sweat glands and sebaceous glands, and thus enhance skin luster and elasticity. Modern explanations for its therapeutic mechanisms are:
Regulate nervous system: Massage helps balance the nervous system by soothing or stimulating the nerve endings, resulting in different physiological responses that lead to healing.
Improve blood and lymph circulation: The rhythmical manual pressure and movement used in massage not only creates a pumping effect on the blood and lymph flows, but also enhances the biological activities of the components. For example, studies show that after massage, changes in the blood include a raised white blood count, higher endocytosis action, and increased blood volume.
Promote bio-active ingredient release: Massage enhances the secretions of bio-active ingredients like endorphins and serotonin (5-HT), which relieve painful conditions. Massage also lowers the body’s catecholamine level, which means certain actions of neurotransmitters and hormones in the sympathetic nerves are inhibited, resulting in some important physiological activities slowing down, and the body becomes relaxed.
Speed up tissue healing: Massage helps to ease pain, promote local circulation, relieve swelling, prevent tissue wasting and adhesions, which all facilitate the healing process of damage tissues.
Increase metabolism: Massage increases the body’s secretions and excretions; for example, it promotes the production of gastric juices, saliva and urine. It also promotes gas exchange in the lungs, and other physiological activities inside the body. These reflect an overall increase in the metabolic rate.
Enhance mobility and flexibility: The stretching of the muscles and connective tissues in massage helps keep the tissues elastic and firm.


